Energy recovery from waste is the conversion of non-recyclable waste materials into useable heat, electricity, or energy such as fuel through a variety of processes, including combustion, gasification, pyrolization, anaerobic digestion, and landfill gas (LFG) recovery. This process is often called waste-to-energy (WTE). Currently there are 86 facilities in the United States for combustion of municipal solid waste (MSW), with energy recovery. No new plants have been built in the US since 1995, but some plants have expanded to handle additional waste and create more energy. The 86 facilities have the capacity to produce 2,720 megawatts of power per year by processing more than 28 million tons of waste per year. Mass burn facilities are by far the most common types of combustion facilities in the United States. A mass burn facility is a type of municipal solid waste (MSW) incineration, or waste-to-energy (WTE), facility in which MSW is burned with only minor presorting to remove oversized and noncombustible items, and hazardous or explosive materials.
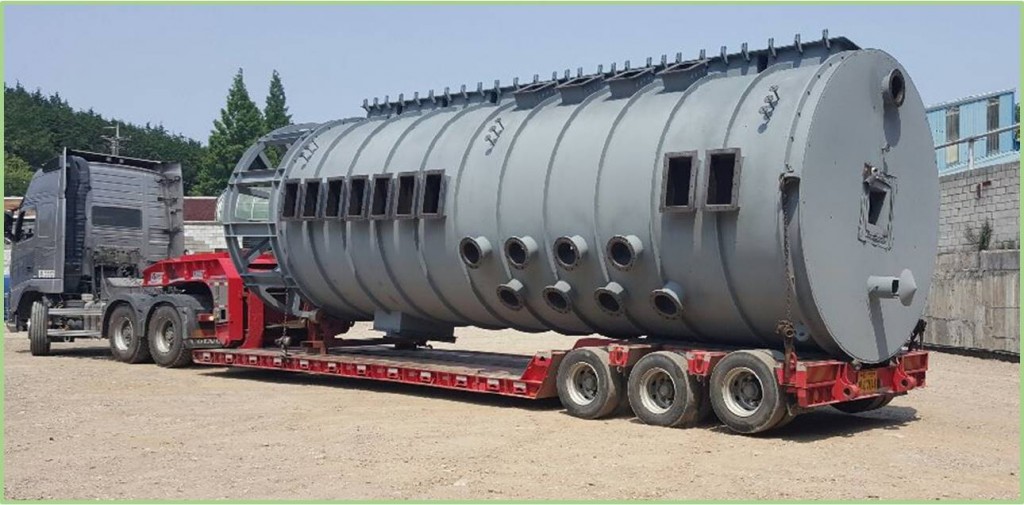

Contrastively in South Korea, as a company specializing in Disk Rotary Multiple Stage, “ILYANG ENG” has excellent technology to dry wastewater, sewage sludge and food wastes that pollute the environment and recycle them as fuel coal, feedstuff and compost. Currently, ILYANG ENG can do four ways to save energy with using of the Multistage Disk Dryer Rotary (MDDR). First, they are using the air knife (dry wind) in the MDDR to increase the drying efficiency. Second, there is energy saving method through the cross sectional area increment (Scatter) in the MDDR. They cut the sludge into small pieces to increase the efficiency of the drying process. Third, through bucket conveyor (recovered), Reduce moisture and viscosity by mixing dry sludge. Finally, through heat recovery in the MDDR, it would be able to save energy. CEO Soo-hyuk Choi of ILYANG ENG stated that waste materials should be disposed in any way, and somebody should do it. In the case of the US, they have an expansiveness of the landscape and high technical skills for the disposal of waste-materials. On the other hand, in the case of South Korea they have been difficulties; such as lack of landfill, odor occurs when incineration of waste materials, economic problem etc. The MDDR was created to overcome these limitations. The MDDR has the advantage that it does not smell and smoke when incinerated the waste materials, and characterized economically feasible. We have to pay close attention to companies like ILYANG ENG, which realized waste-to-energy in poor surrounding environment differs from developed countries.

▲ ILYANG ENG Co., Ltd
▲ Brand Name: Disk Rotary Multiple-Stage
▲ CEO : Soo-hyuk Choi
▲ T : +8210-4550-7698
▲ E-mail : soohyuk2016@naver.com
▲ www.ilyangmpf.com
Irene Kim
K-Herald Korea
(Los Angeles Times Advertising Supplement)

