
Japan’s Ministry of Economy and Industry has spent $9.2 billion to establish a new 20-nano semiconductor foundry plant near Kumamoto Prefecture, where SONY’s CMOS (Complete Metal-oxide-Semiconductor) Image Sensor plant is currently located. This will be done in a joint venture between SONY and Taiwan within 2021. TSMC will most likely be more dominant in the initiative while Japanese companies other than SONY Group may also participate with some investment. This will be the first factory in Japan that produces sub 40-nano semiconductors. The investment burden is to be borne by SONY Group while TSMC is in charge of the manufacturing process. In addition, the processing plant will be established in Kumamoto Prefecture.

If the two companies agree to establish the joint foundry plant, TSMC will have its first production plant in Japan. SONY will be able to reliably receive their CMOS Image Sensor chips directly.
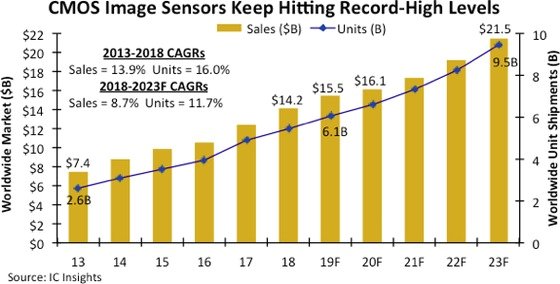
The CMOS Image Sensor is a low-power consumption image sensor that has brightened prospects for the CMOS Image Sensor (CIS) market. This sensor is commonly found in mobile devices such as 5G smartphones, high-resolution digital cameras, medical imaging devices, self-driving car surveillance cameras, and robots. According to global consulting firm KPMG, the overall sensor market, including CIS, is expected to grow 12% annually from last year’s $47 billion to $143 billion by 2030. Currently, SONY’s CIS is thriving in the global competitive market for semiconductors. SONY has an unrivaled No. 1 share in the global CIS market exceeding 48%. SONY’s annual revenue from CMOS Image Sensor is close to $9 billion.
SONY, which started as a radio repair shop at Tokyo’s Nihonbashi Department Store in 1946, has won several titles as “the world’s first”. The world’s first portable transistor radio (TR-55) was released in 1957, the world’s first commercial transistor TV (TV8-301) in 1960, and in 1968 it set a standard for high-end monitors with TRINITRON. This served as the foundation for SONY’s dominance in the TV market for nearly 30 years. The cassette tape player ‘WALKMAN’, released in 1979, sold a total of 220 million units worldwide until its discontinuation in 2003. Sony was the first to successfully commercialize digital cameras in 1981, and the first CD was invented in collaboration with Philips in 1982. In 1991, they succeeded in commercializing its first lithium-ion battery. SONY’s impact on the tech market was greater than Apple’s.
By 1987, SONY had already taken control of the technology industry. They pursued a new goal of creating a “SONY ecosystem” by focusing on digital content. After acquiring CBS Records International in 1988, SONY Music Entertainment was created, and in 1989 they acquired COLUMBIA Pictures. In 1993, SONY Computer Entertainment was founded and released the first PlayStation, a game console. In 1995, SONY heavily invested in the digitalization of movies and music. They ran So-Net (digital file internet service) and PressPlay (online music shop), and in 1996, they launched a series of VAIO laptops with digital content made available.
However, between 2012 and 2017, SONY Chemical, PC, TV, and battery divisions were separated or sold, this greatly reduced the manufacturing power. While this was their main business in the past, SONY directed their focus on service industries such as games, movies, music and finances. From April 2021, SONY Group changed its business governance structure by establishing Sony Group Corporation as a holding company that takes charge of overall business structure management and strategy and comprises Sony Semiconductor Solutions, Sony Entertainment (Sony Pictures, Sony Music), Sony Interactive Entertainment, Sony Financial Holdings, and others. Currently, games account for 31% of SONY’s total sales, 19% of movies/music, 22% of electronics/IT, and 28% of finance.
Since the launch of the Playstation 1 in 1996, it sold over 500 million units, which accounted for 46% of gaming consoles. When the Playstation 5 released in November of 2020, it was able to exceed the Playstation 4’s 12 week sale in 12 hours and sold 4.5 million units in its first month. The PlayStation 5 uses a processor designed by AMD (U.S.) and the 7nm processor is manufactured by TSMC (Taiwan). It is then tested and packaged by ASE (Taiwan). Sony has a deep business relationship with TSMC. Sony also provides a $60 monthly subscription to their PlayStation Plus membership with 46 million active members; 3 times the amount of Microsoft’s XBOX live members.
In the TV and film industry, SONY’s subsidiary Aniplex’s animation, “The Blade of the Dead” topped the global box office with $500 million. It acquired Crunchyroll, an anime streaming service with 90 million subscribers in 200 countries, to secure growth potential. They also own the rights to the character, “Spider-Man.”
In the music category, SONY Music acquired EMI, a world-renowned record label, with a total of 4.8 million copyrights, including The Beatles, Michael Jackson, Queen, and The Rolling Stones.
In the electronics category, the CIS recorded $9 billion in sales in 2020. This accounts for 46% of the global market share. The global pandemic has led to a surge in demand for smartphones and self-driving cars.
With that said,the Japanese government and SONY desperately need the establishment of TSMC’s manufacturing plant in Japan. The pandemic has given hope to the Japanese semiconductor industry, which has been in a long recession. Sony expects their products to become more relevant. It is worth looking forward to SONY and Japan’s semiconductor industry’s resurgence.
Japanese government tries to consolidate its shares in CIS market by supporting SONY, the unrivaled player in CIS sector, and attracting TSMC, the world’s strongest foundry player, in the country. By doing this, the government maps out its scheme to enter other semiconductor markets in the future. In addition, there is also a possibility that SONY will seek a new path in another area: ‘vehicle semiconductor’. Currently, Japan’s most advanced semiconductor plant is Renesas Electronics’ 40-nanometer plant, which focuses on automotive semiconductors, with its global share of 20-30%.
It seems that TSMC also has their interest in the Japanese automotive semiconductor industry. Japan’s new manufacturing plant is expected to ease the supply-chain risk of automakers being forced to cut production due to the lack of semiconductors. This will also benefit Renesas Electronics, which is a large automotive semiconductor company that is partially manufactured by and entrusted to TSMC.
Mike Choi
Asia Journal
(Los Angeles Times Advertising Supplement)

